Jeep VIN Decoder
Don’t risk hidden issues! Click ‘Check Any VIN Now’ to see recalls, problems, issues, and more! Just enter your VIN and email to get your report.
Free Jeep VIN Decoder
Your Ultimate Guide To A Jeep VIN Decoder!
The rugged capability and iconic design of a Jeep are undeniably appealing, but before you commit, you need to know the whole story. A Jeep’s Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is the key to unlocking that story, revealing everything from its original factory specifications to its past adventures (and potential problems). This guide is your ultimate resource for decoding Jeep VINs. We’ll make sure you can make informed decisions whether you’re eyeing a brand new Wrangler or a classic CJ.
We’ll take you deep into the world of Jeep VIN decoding, covering everything you need to know:
- What is a Jeep VIN Decoder? We’ll explain how this 17 character code acts as a unique identifier for every Jeep.
- Decoding Your Jeep VIN: We’ll break down each character and its meaning, revealing the secrets hidden within the code, including information specific to Jeeps like trim level (Sport, Sahara, Rubicon, etc.), 4×4 system (Command-Trac, Selec-Trac, etc.), and factory options.
- Free vs. Paid Jeep VIN Decoders: We’ll explore both free and paid options to help you choose the best tool for your needs, considering the level of detail each provides. Some paid decoders may offer access to Jeep specific databases or historical records.
- Jeep VIN Structure: Understand the organization of the 17 characters and what each section signifies, including the World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI) specific to Jeep and what it tells you about where your Jeep was manufactured.
- Where to Find Your Jeep VIN: We’ll show you the common locations for finding the VIN on different Jeep models, from the windshield to the frame rail. We’ll also discuss where to find it on older models, which can sometimes be tricky.
- Decoding Specific Jeep Codes: We’ll delve into the specific codes used by Jeep, explaining what they reveal about the vehicle’s origin, engine type (e.g., the Pentastar V6, the EcoDiesel, or the various HEMI engines), transmission, and more. This could include details about special editions like Willys, High Altitude, or 80th Anniversary models.
- Jeep Specific Information: Beyond the basic VIN, we’ll discuss resources for researching Jeep build sheets, which can provide even more granular detail about the original configuration of your Jeep, including options, colors, and even the original dealer. This is particularly helpful for classic Jeeps and restoration projects.
- Checking for Jeep Recalls: We’ll cover how to use your VIN to check for any outstanding recalls on your Jeep, ensuring its safety and reliability. This is crucial, especially for older models.
- Jeep Forums and Communities: We’ll mention online Jeep communities and forums where you can connect with other owners and experts, often willing to help decode VINs and provide insights into specific models. These communities are invaluable resources.
What Is A Jeep VIN Decoder
A Jeep VIN decoder is a specialized tool – either a website, software, or even a knowledgeable enthusiast—that translates the seemingly random 17 character Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) on a Jeep into meaningful information about that specific vehicle.
It’s like a secret code-breaker for your Jeep. Instead of just seeing a string of letters and numbers, a VIN decoder reveals details like the Jeep’s original factory specifications (engine, transmission, trim level, options, paint color, etc.), where it was manufactured, and sometimes even its production date. For Jeeps specifically, a good VIN decoder can be particularly valuable because it can differentiate between the numerous trim levels (Sport, Sahara, Rubicon, etc.), 4×4 systems, special editions, and engine options that are unique to the Jeep brand. It’s more than just a generic car decoder; it’s tailored to the intricacies of Jeeps.
Table of Contents
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Wrangler (YJ, TJ, JK, JL)
(1987–Present)
- Dashboard: Lower-left windshield, visible from outside.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, on a factory sticker.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or near the front strut tower.
- Chassis Frame: Stamped on the driver’s side frame rail near the front wheel.
- Paperwork: Listed in registration, insurance, and service records.
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Grand Cherokee (ZJ, WJ, WK, WL)
(1993–Present)
- Dashboard: Lower-left windshield, visible from outside.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, on a factory sticker.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or near the radiator support.
- Chassis Frame: Located on the driver’s side frame rail (older models).
- Paperwork: Found in title, registration, and warranty documents.
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Cherokee (XJ, KJ, KL)
(1974–Present)
- Dashboard: Lower-left windshield, visible from outside (post-1981 models).
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, on the factory sticker.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or near the front crossmember.
- Frame Rail (Older Models): Some classic Cherokees have the VIN stamped on the front chassis.
- Paperwork: Listed in registration, title, and service records.
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Gladiator (JT)
(2020–Present, Classic 1962–1988)
- Dashboard: Lower-left windshield, visible from outside.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, near the latch.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or front subframe.
- Frame Rail (Older Models): Stamped on the front left frame rail.
- Paperwork: VIN is found in registration, insurance, and warranty records.
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Renegade
(2015–Present)
- Dashboard: Lower-left windshield, visible from outside.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, on the factory sticker.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or radiator support.
- Paperwork: Found in title, registration, and service records.
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Compass
(2007–Present)
- Dashboard: Lower-left windshield, visible from outside.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, near the latch.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or front crossmember.
- Paperwork: Listed on registration, insurance, and warranty documents.
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Patriot
(2007–2017)
- Dashboard: Lower-left windshield, visible from outside.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, near the latch.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or near the front strut tower.
- Paperwork: VIN is found in registration, title, and service records.
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Wagoneer / Grand Wagoneer
(1963–1991, 2022–Present)
- Dashboard (Modern Models): Lower-left windshield, visible from outside.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, near the latch.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or near the radiator support.
- Older Models (Pre-1981): May have the VIN stamped on the chassis frame rail.
- Paperwork: VIN appears in registration, title, and maintenance records.
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Liberty (KJ, KK)
(2002–2012)
- Dashboard: Lower-left windshield, visible from outside.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, near the latch.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or radiator support.
- Paperwork: Found in registration, insurance, and service records.
Where To Find The VIN On A Jeep Commander (XK)
(2005–2010)
- Dashboard: Lower-left windshield, visible from outside.
- Driver’s Side Door Frame: Inside the driver’s door jamb, near the latch.
- Engine Bay: Stamped on the firewall or near the front crossmember.
- Paperwork: VIN is found in title, registration, and service records.
Decoding Jeep Model Codes
Wrangler
- CJ-2A (1945–1949): The original civilian Jeep, a WWII veteran turned adventurer.
- CJ-3A (1949–1953): Refined design, still carrying its military DNA.
- CJ-3B (1953–1968): Taller hood to house a more powerful engine.
- CJ-5 (1955–1983): The iconic Jeep, a long-running symbol of freedom.
- YJ Wrangler (1987–1995): The first official Wrangler, known for its square headlights.
- TJ Wrangler (1997–2006): Round headlights returned, plus updated suspension.
- LJ Wrangler (2004–2006): A longer Wrangler, offering more space.
- JK Wrangler (2007–2018): Modern engines, tech, and the four-door option.
- JKU 4-Door (2007–2018): The game-changing four-door Wrangler.
- JL Wrangler (2018–present): The latest generation, with improved efficiency and off-road prowess.

Cherokee
- SJ Cherokee (1974–1983): Started as a sporty two-door, later adding a four-door option.
- XJ Cherokee (1984–2001): Groundbreaking unibody design, legendary off-road capability.
- KL Cherokee (2014–2023): Modern compact SUV, blending city comfort and off-road potential.

Grand Cherokee
- ZJ Grand Cherokee (1993–1998): The original Grand Cherokee, upscale and offering V8 power.
- WJ Grand Cherokee (1999–2004): Improved suspension, blending luxury and off-road.
- WK Grand Cherokee (2005–2010): Car-like handling with off-road capability.
- WK2 Grand Cherokee (2011–2022): Advanced engines like the Pentastar and EcoDiesel.
- WL Grand Cherokee (2022–present): Latest model, modern tech and enhanced off-road.

Wagoneer | Compass | Gladiator | Renegade | Liberty | Comander | Avenger
Wagoneer:
- SJ Wagoneer (1963–1983): Full size luxury SUV.
- WS Wagoneer/Grand Wagoneer (2021–present): Modern full size luxury.
Compass:
- MK Compass/Patriot (2007–2017): Compact SUVs, fuel efficient.
- MP Compass (2017–present): Redesigned compact crossover.
Gladiator:
- JT Gladiator (2019–present): Wrangler based pickup.
Renegade:
- BU Renegade (2015–present): Compact SUV, rugged off road.
Liberty:
- KJ Liberty (2002–2007): Compact SUV, independent suspension.
- KK Liberty (2008–2012): Updated KJ.
Commander:
- XK Commander (2006–2010): Three row Jeep.
- WK2 Commander (2018–2022): Extended version.
- H1/H6 Commander/Meridian (2021–present): Mid size SUVs.
Avenger:
- JJ Avenger (2023–present): Electric compact SUV.

Jeep VIN Locations
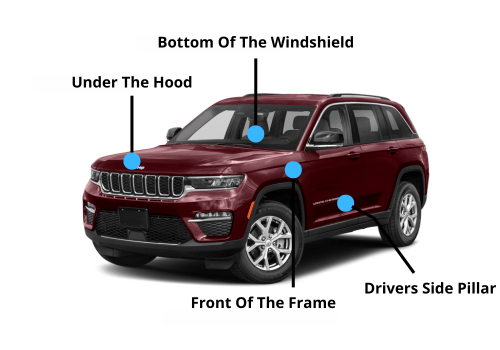
Jeep VIN Decoder - All Codes
Country of Origin
| Code | Country |
|---|---|
| 1 | USA |
| 2 | Canada |
| 3 | Mexico |
Manufacturer
| Code | Manufacturer |
|---|---|
| C | Chrysler Corporation (Jeep Division) |
| J | Jeep (Stellantis) |
Model Line and Years
| Model | Years |
|---|---|
| CJ-2A | 1945–1949 |
| CJ-3A | 1949–1953 |
| CJ-3B | 1953–1968 |
| CJ-5 | 1955–1983 |
| YJ Wrangler | 1987–1995 |
| TJ Wrangler | 1997–2006 |
| LJ Wrangler | 2004–2006 |
| JK Wrangler | 2007–2018 |
| JL Wrangler | 2018–present |
| SJ Cherokee | 1974–1983 |
| XJ Cherokee | 1984–2001 |
| KL Cherokee | 2014–2023 |
| ZJ Grand Cherokee | 1993–1998 |
| WK Grand Cherokee | 2005–2010 |
| JT Gladiator | 2019–present |
| BU Renegade | 2015–present |
Manufacturing Plant
| Code | Plant |
|---|---|
| T | Toledo, Ohio, USA |
| B | Brampton, Ontario, Canada |
| S | Saltillo, Mexico |
| G | Graz, Austria |
How To Decode a Jeep VIN
WMI (World Manufacturer Identifier)
The first three characters of the VIN indicate the vehicle’s country of origin and manufacturer.
Country of Origin (Position 1):
1 = USA 2 = Canada 3 = Mexico
Manufacturer (Position 2):
C = Chrysler (Jeep models, North America) J = Jeep (Outside North America)
Vehicle Type (Position 3):
Varies based on the specific vehicle type and model.
VDS (Vehicle Descriptor Section)
The next six characters (positions 4-9) provide information about the vehicle’s model, body style, engine type, and other key details.
Model Line and Drive Type (Position 4):
J = Jeep Wrangler, Jeep Cherokee K = Jeep Grand Cherokee L = Jeep Compass M = Jeep Renegade, Jeep Gladiator
Body Type or Trim Level (Position 5):
Varies based on specific models and configurations.
Trim Level or Body Type (Position 6):
Varies based on specific models and configurations.
Restraint System or GVWR (Position 7):
Varies based on specific models and configurations.
Engine Type (Position 8):
Varies based on specific models and configurations.
VIS (Vehicle Identifier Section)
The final eight characters provide further identification details.
Check Digit (Position 9):
A security code used to verify the authenticity of the VIN.
Model Year (Position 10):
A = 1980, B = 1981, …, Y = 2000 1 = 2001, 2 = 2002, …, 9 = 2009 A = 2010, …, L = 2020, M = 2021, …, Y = 2030
Manufacturing Plant (Position 11):
C = Belvidere, Illinois, USA (Jeep Cherokee, Compass, and Renegade) D = Detroit, Michigan, USA (Jeep Grand Cherokee, Jeep Wagoneer) T = Toledo, Ohio, USA (Jeep Wrangler, Jeep Gladiator)
Vehicle Production Sequence Number (Positions 12-17):
A unique serial number assigned to each vehicle as it comes off the production line.
How To Interperet Different VIN Characters
First Character – Country of Manufacture
The first character indicates where the vehicle was built. This is especially important for Jeeps, as they’ve been manufactured in various locations throughout their history.
- 1 = USA
- 2 = Canada
- 3 = Mexico
- J = Japan (for some models)
- Other codes may exist depending on the specific Jeep model and era. Research is key.
Second Character – Manufacturer
The second character identifies the manufacturer. For Jeep, this typically represents Chrysler (now part of Stellantis), but it can change due to corporate mergers and acquisitions. Again, confirm the specific code for the Jeep you’re researching.
Third Character – Vehicle Type
This character describes the vehicle type. Jeep uses a variety of codes, and it’s not always a simple classification. It relates to the general vehicle type (e.g., passenger car, truck, SUV), but the specific meaning can vary.
Characters 4 to 8 – Vehicle Descriptor Section (VDS)
These five characters provide crucial details about the Jeep, including model line, body style, engine, and trim. This is where the most Jeep specific information resides.
- Model/Series (Position 4): Might indicate the general model family (e.g., Wrangler, Cherokee, Grand Cherokee).
- Body Style/Trim (Position 5): Often related to the number of doors or a general trim level. Jeep’s trim levels (Sport, Sahara, Rubicon, etc.) are complex, so this isn’t always a direct correlation.
- Trim/Equipment (Position 6): Can be related to trim level and options. Jeep has a wide range of options, and this character may reflect some of them.
- Restraint System/GVWR (Position 7): Relates to safety features and weight rating.
- Engine Type (Position 8): Extremely important for Jeeps. This identifies the engine (e.g., 3.6L Pentastar V6, 2.0L Turbo, various HEMI engines). Jeep has used many different engines over the years, making this code vital.
Ninth Character – Check Digit
A security code used to verify the VIN’s authenticity.
Tenth Character – Model Year
Indicates the vehicle’s model year. Jeep uses the standard VIN system.
Eleventh Character – Assembly Plant
Identifies the factory where the Jeep was assembled. This is very relevant for Jeeps, as different models are made in different plants.
Characters 12 to 17 – Serial Number
A unique production number for the specific vehicle.
Example Jeep VIN Breakdown (Hypothetical):
VIN: 1C4JPWLM9K123456
- 1 = Built in the USA
- C = Chrysler (or related manufacturer)
- 4 = Vehicle type (specific meaning varies)
- J = Jeep model designation (specific meaning varies)
- P = Body style/trim (specific meaning varies)
- W = Trim/equipment (specific meaning varies)
- L = Engine type (very important!)
- M = Restraint system/GVWR
- 9 = Check digit
- K = Model year (refer to the year code chart)
- 1 = Assembly plant (specific meaning varies)
- 23456 = Unique serial number
Free Jeep VIN Decoder
Free VIN decoders often pull from publicly available databases, which can be limited. They might give you basic information like the year, make, and model, but often lack details about trim level, options, and vehicle history. Also, the quality of free decoders can change as websites and data sources are updated (or become outdated).
However, some commonly mentioned and generally reputable free VIN decoder websites include:
- Jeep VIN Decoder (official webiste): Mopar (the service, parts, and customer care organization for Stellantis, which owns Jeep) does have a VIN lookup tool on their website. You can find it by searching “Mopar VIN Lookup” or going to their site and looking for the “My Vehicle” section.
- NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration): The NHTSA site is a good starting point, primarily for checking recalls. It’s not a full decoder in the sense of giving you all the vehicle’s original specs, but it’s essential for safety information.
- AutoCheck: AutoCheck offers a free VIN check that provides a limited amount of information. They will, however, try to upsell you to their paid service for a more detailed report.
- Carfax: Similar to AutoCheck, Carfax offers a limited free VIN check that can give you a basic overview. They also push their paid service for more comprehensive reports.
Limitations Of A Free Jeep VIN Decoder
Incomplete Information: Free decoders often only provide basic information like year, make, and model. They frequently lack details about trim level (Sport, Sahara, Rubicon, etc.), specific factory options, special editions, and other Jeep specific nuances. This is a huge limitation for Jeeps, as trim levels and options significantly impact value and desirability.
Inaccurate or Outdated Data: The data used by free decoders might not be entirely accurate or up to date. Databases can have errors or lag behind changes in vehicle information. This can be especially problematic for older Jeeps where records might be less reliable.
Lack of Vehicle History: Free decoders generally don’t provide any vehicle history information (accidents, title issues, etc.). While some might offer a very basic check, it’s usually just a teaser to upsell you to a paid history report. For a used Jeep, knowing its history is crucial.
Information You Can Get from Free Jeep VIN Decoders
- Year: The model year of the Jeep. This is usually accurate.
- Make: Obviously, it will confirm that it’s a Jeep.
- Model: The general model designation (e.g., Wrangler, Cherokee, Grand Cherokee). However, it might not be specific about the submodel or trim level (e.g., Wrangler Sport vs. Wrangler Rubicon).
- Engine (Sometimes): Some free decoders might give you a general engine designation (e.g., “V6” or “4 cylinder”), but they rarely provide the exact engine code or displacement (e.g., 3.6L Pentastar V6).
- Manufacturing Country: Where the Jeep was manufactured.
- Body Style (Sometimes): Might indicate the general body style (e.g., 2-door, 4-door, SUV, pickup).
- Very Basic Specs (Sometimes): Some decoders might give you a few very basic specs, but these are often generic and not specific to the actual vehicle’s configuration.
Best Jeep VIN Decoders
- carVertical is a popular VIN decoder that focuses on providing a comprehensive vehicle history report. They often emphasize uncovering hidden damage, mileage rollbacks, theft records, and maintenance history. Some users have found their reports quite detailed.
Mopar VIN Decoder (Official Jeep/Chrysler/Dodge/Ram): This is the official VIN decoder from the manufacturer. It is often considered the most reliable source for original factory specifications, including the year, make, model, engine, transmission, original equipment, and sometimes even the original dealer where the vehicle was sold. It generally doesn’t provide accident history or ownership records, but it’s the gold standard for factory information. The Mopar site can sometimes be a bit tricky to navigate to find the VIN decoder.
EpicVin: This is another well known and widely used VIN decoder. EpicVin aims to provide comprehensive vehicle history reports, including accident history, title issues, odometer readings, and more. They often pull data from multiple sources to provide a more complete picture of the vehicle’s past.
AutoCheck: Run by Experian, AutoCheck is a popular paid service. It focuses on providing a vehicle history report and a risk assessment score. AutoCheck often offers a competitive price and can be bundled with other Experian services.
VINCheck.info: This is a free VIN decoder tool that allows users to look up basic information about a vehicle using its VIN. While the free service may provide some useful information, it is generally less comprehensive than paid options like carVertical or AutoCheck.
Benefits Of A Using Paid VIN Decoder
Accident History: Paid reports are far more likely to include detailed accident records, including the severity of the damage, police reports, and insurance claims. Free decoders often only indicate if the vehicle has been reported as salvaged or totaled, without specifics.
Title Issues: Paid decoders uncover title problems like salvage titles, flood damage titles, rebuilt titles, odometer rollback, liens, and more. This is crucial for understanding the true legal status of the vehicle.
Odometer Readings (Mileage History): Paid reports track the vehicle’s mileage over time, which helps detect potential odometer fraud (rollback). They often show the mileage recorded at various points throughout the vehicle’s life (e.g., inspections, service visits).
Ownership History: Paid reports often provide information about the number of previous owners, the states the vehicle was registered in, and the length of ownership periods. This can give you insights into how well the vehicle was maintained and if it was frequently sold.
Service and Maintenance Records: Some paid reports are now able to pull information on service and maintenance records, though the extent and accuracy of this data can vary significantly. This can give you an indication of how well the car was maintained.
Access to More Databases: Paid VIN decoders typically access a wider range of databases, including government agencies, insurance companies, salvage auctions, and commercial data providers. This gives them a more complete picture of the vehicle’s history.
Data Verification: Paid services often have processes in place to verify and cross reference data from multiple sources, which helps to reduce the risk of errors or omissions.
Where Do i Find The VIN Number On My Jeep
Driver’s Side Dashboard: This is the most common and easily accessible location. Stand outside the vehicle, on the driver’s side, and look at the lower corner of the dashboard where it meets the windshield. The VIN should be visible through the windshield.
Driver’s Side Doorjamb: Open the driver’s side door and look on the doorjamb (the vertical part of the doorframe). There should be a sticker containing the VIN, along with other vehicle information.
Vehicle Title and Registration: The VIN will be printed on your vehicle’s title and registration documents.
Insurance Card: The VIN should also be listed on your car insurance card or policy.
Engine Compartment: On some older Jeeps, the VIN may be stamped on a metal plate or sticker located in the engine compartment. This is less common on newer models.
Frame: On some older vehicles, the VIN may also be stamped directly onto the vehicle frame.
I Can't Find My Jeep VIN
Dashboard (from Inside the Vehicle): Sometimes the angle of the sun or the placement of items on the dashboard can obscure the VIN. Try looking at it from different angles from inside the Jeep.
Doorjamb – Both Sides: Check both the driver’s and passenger’s side doorjambs. While it’s most often on the driver’s side, it could have been moved or duplicated.
Under the Hood – Firewall: Carefully inspect the firewall (the metal panel separating the engine compartment from the passenger cabin). Look for a metal tag or sticker. Clean the area if it’s dirty. Use a flashlight.
Under the Hood – Inner Fenders: Sometimes, especially on older vehicles or those that have had body work, a partial VIN might be stamped on the inner fender wells. This is not a primary location, but it’s worth a check if you’re desperate.
Glove Box: Some older vehicles had a sticker or plate with the VIN inside the glove box.
Inside the Console: Check inside the center console (if the Jeep has one).
Frame Rail (Driver’s Side, Front): On older Jeep models, a partial VIN (or sometimes the full VIN) might be stamped directly into the driver’s side frame rail, near the front of the vehicle. You’ll likely need to get on your hands and knees and use a flashlight. Clean the frame rail with a wire brush or solvent to remove dirt and rust.
Frame Rail (Passenger’s Side, Rear): Similarly, check the passenger’s side frame rail near the rear of the vehicle.
Frame Near Suspension Mounts: Inspect the frame in areas near suspension mounts.
Frame, Top of Rail: On some models, the VIN might be stamped on the top of the frame rail, which means you’d need to get underneath the vehicle and look upwards.
Service Records: Check any service records that came with the vehicle. The VIN should be listed on them.
Previous Owner: If possible, contact the previous owner. They might know the VIN or have documentation.
How Do I Find the VIN in the Jeep app (Bluelink)
- Open the Jeep App: Launch the Jeep app on your smartphone or tablet.
- Log In (If Necessary): Enter your username and password to log in to your account.
- Select Your Vehicle: If you have multiple Jeeps connected to your account, make sure you select the correct vehicle. There’s usually a vehicle selection area on the app’s main screen. It might be a dropdown menu or a carousel of your vehicles.
- Look for Vehicle Details/Information: The location of the VIN information within the app can vary slightly depending on the app version and specific vehicle features, but generally, you should look for something like: “Vehicle Details”, “Settings” and then “Vehicle Information”, “Vehicle Info” or “My Vehicle”.
- Find the VIN: Once you’re in the vehicle information section, scroll down or look for a field labeled “VIN” or “Vehicle Identification Number.” The 17 character VIN should be displayed there.
Discover the value of your cars options and specification!
- Select from thousands of vehicles and options
- See how each option adds value to your car
- Discover which tech features add a premium
- Spot which options hold their value over time
- Find out if that 'Sport' package pays off later
- Identify high value features others miss
$355 $354 $353 $352 $351 $350
How to Check for Jeep Recalls by VIN: A Step by Step Guide
1. Locate Your VIN:
2. Go to the NHTSA Website:
- The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) is a great resource. Visit their website at www.nhtsa.gov/recalls.
3. Enter Your VIN:
- On the NHTSA recalls page, you’ll find a section to check for recalls by VIN. Enter your 17 digit VIN carefully and accurately.
4. Check the Results:
- The NHTSA site will search its database and tell you if there are any open recalls for your Jeep. It will provide details about the recall, including the affected components and what needs to be done.
5. Check the Mopar Website (Optional):
- Mopar, the service and parts division for Stellantis (which owns Jeep), also has a VIN lookup tool on their website. You can find it by searching “Mopar VIN Lookup” or going to their site and looking for the “My Vehicle” section.
- This can sometimes provide additional information or confirmation of recalls.
6. Contact a Dealership:
- If you find any open recalls for your Jeep, contact your local Jeep dealership to schedule a free repair. Recalls are typically covered by the manufacturer, so you shouldn’t have to pay for the repair.
Useful Resources For Checking A Jeep Recall
Mopar VIN Decoder (Official Chrysler/Dodge/Jeep/Ram):
Purpose: Obtain the original factory build information for your Jeep. This includes the year, make, model, engine, transmission, original options, and sometimes even the original dealership.
Link: While there isn’t a single, official “Mopar VIN Decoder” page that’s always easy to find (the sites change over time), you can usually find a free decoder by searching “Mopar VIN decoder” on Google. Look for links that direct to Mopar’s official website or a Stellantis site. Be aware that you might need to navigate through their menus to find the tool.
2. Comprehensive Vehicle History Reports (Paid Services):
carVertical:
Focus: Comprehensive vehicle history, emphasizing hidden damage, mileage fraud, and accident history.
EpicVin:
Focus: Wide range of data sources, including accident history, title issues, and odometer readings.
AutoCheck (Experian):
Focus: Vehicle history reports and risk assessment scores. Owned by Experian, so data is likely comprehensive.
CARFAX:
Focus: Well established vehicle history reporting service with a large database.
Jeep Forums and Communities
WranglerForum.com (for Wrangler owners)
JeepGarage.org (for Grand Cherokee owners)
Also Search “[Your Jeep Model] forum” on Google to find specific communities)
Common Jeep Recalls To Be Aware Of
Common Recall Areas (across various Jeep models and years):
Airbags: Takata airbag inflators have been a widespread issue affecting many manufacturers, including Jeep. These inflators can degrade over time and explode during deployment, sending shrapnel into the vehicle. This is one of the most critical recalls to check for.
Fuel System: Fuel leaks can occur due to various issues, such as faulty fuel lines, fuel pump modules, or fuel tank designs. Fuel leaks pose a fire risk.
Electrical System: Electrical problems can range from faulty wiring harnesses to issues with the powertrain control module (PCM) or other electronic components. These can cause stalling, loss of power, or even fires.
Brakes: Brake system issues can include problems with the anti-lock braking system (ABS), brake booster, or brake lines. These can compromise braking performance.
Steering: Steering problems can involve issues with the power steering system, steering column, or steering linkage. These can affect vehicle control.
Software Glitches: Modern Jeeps rely heavily on software. Software glitches can cause a variety of problems, from malfunctioning infotainment systems to issues with engine performance or safety features.
Transmission: Transmission problems can include issues with the transmission software, transmission control module (TCM), or the transmission itself.
Rollaway Risk: Some Jeeps have been recalled for issues that could cause the vehicle to roll away when parked, especially on an incline.
Seat Issues: Some recalls relate to seat track welds failing or headrests not performing to standard.
Examples of Specific Recalls (Check NHTSA for Current Status):
Jeep Wrangler (JL): Recalls have addressed issues with the frame welds, steering, airbags, and fuel leaks.
Jeep Grand Cherokee (WK2): Recalls have addressed issues with the braking system, electrical system, rollaway risk, and airbags.
Jeep Cherokee (KL): Recalls have addressed issues with the transmission, airbags, and windshield wiper motor.
Jeep Compass (MP): Recalls have addressed issues with the engine stalling and airbags.
How to Check for Recalls (Most Important Step):
Go to the NHTSA Website: Visit the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) website: https://www.nhtsa.gov/recalls
Enter the VIN: Enter the 17-digit Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) in the designated field.
View Recall Information: The website will display any open recalls for that specific vehicle. It will provide details about the recall, the affected components, and the remedy.
Jeep Warranty Check by VIN: How to Find Your Coverage
Official Mopar/Jeep Warranty Information
Contact a Jeep Dealership: The most reliable way to check your Jeep’s warranty status is to contact a local Jeep dealership’s service department. Provide them with the VIN, and they can access the official Mopar warranty database to determine the coverage. This is generally the most accurate method.
Mopar Owner Connect: The Mopar Owner Connect website should provide warranty information after you register and add your vehicle using its VIN. However, user experience varies, and some have reported that this method isn’t always 100% reliable or up to date. Try this link: https://www.mopar.com/en-us/care/owners-manuals.html (You will likely have to navigate through the site after you log in).
Jeep App: If you have a newer Jeep that’s connected to the Jeep app, there may be a section within the app that displays warranty information. (See previous instructions for finding VIN within the app.)
What Is Included In A Jeep Warranty?
Basic Warranty Coverage: You’ll typically receive information about the remaining coverage under the basic factory warranty (usually 3 years/36,000 miles, whichever comes first).
Powertrain Warranty Coverage: You’ll also get details about the powertrain warranty (typically 5 years/60,000 miles, but this can vary).
Additional Warranties: If the vehicle has any extended warranties or other coverage plans, those details should also be provided.
Warranty Start Date: The warranty start date is important, as it determines when the coverage expires. This is usually the original in service date (when the vehicle was first sold or leased).
Transferability: Confirm whether any extended warranties are transferable to a new owner if you are buying a used Jeep.
What to Do If Your Jeep Warranty Has Expired
1. Consider an Extended Warranty:
- Mopar Vehicle Protection: Jeep offers extended warranties through Mopar. These plans can provide coverage for many years or miles beyond your original warranty. They also often include benefits like roadside assistance.
- Third-Party Extended Warranties: Many companies offer extended warranties for vehicles. Research these carefully, as coverage and reliability can vary significantly.
2. Explore Repair Options:
- Independent Mechanics: Find a reputable independent mechanic specializing in Jeeps. They often have lower labor rates than dealerships.
- DIY Repairs: If you’re mechanically inclined, consider doing some repairs yourself. There are many online resources and forums with DIY guides.
- Used Parts: For some repairs, you might be able to save money by using used parts from salvage yards.
3. Maintain Your Jeep:
- Regular Service: Follow the recommended maintenance schedule in your owner’s manual. This can help prevent costly repairs down the road.
- Keep Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance and repairs. This can be helpful if you need to make a claim with an extended warranty company or if you decide to sell your Jeep.
4. Be Proactive:
- Address Issues Early: Don’t ignore small problems. They can often turn into bigger, more expensive issues if left unchecked.
- Research Common Issues: Learn about common problems with your Jeep model. This can help you anticipate potential repairs and budget accordingly.
5. Explore Other Options:
- Jeep Communities: Connect with other Jeep owners online or in person. They can often provide advice on repairs and maintenance.
- Used Car Market: If repairs become too frequent or expensive, you might consider selling your Jeep and buying a newer one with a warranty.
Jeep Budget for Repairs and Maintenance
Regular Maintenance (Per Service – Not Combined Totals):
- Oil Change (Conventional): $50 – $100 (can be lower if you DIY)
- Oil Change (Synthetic): $75 – $150+ (can be lower if you DIY)
- Tire Rotation: $30 – $60
- Fluid Checks/Top Off: $10 – $30 per fluid (often included with other services)
- Brake Inspection: $20 – $50 (often included with oil change)
- Air Filter Replacement: $20 – $50 (can be much higher for specialized filters)
- Spark Plug Replacement (4-cylinder): $100 – $250
- Spark Plug Replacement (6-cylinder): $150 – $400
- Spark Plug Replacement (8-cylinder): $200 – $600+
Potential Repairs (These are HUGE ranges!):
- Brake Pads (per axle): $100 – $400+ (depending on type and complexity)
- Brake Rotors (per axle): $150 – $500+
- Battery Replacement: $100 – $300
- Starter Replacement: $200 – $600
- Alternator Replacement: $250 – $700
- Water Pump Replacement: $300 – $800+
- Radiator Replacement: $400 – $1000+
- Transmission Service: $150 – $500+ (depending on the type of service)
- Transmission Replacement/Rebuild: $2,000 – $6,000+
- Engine Repair/Rebuild: $2,000 – $8,000+ (or more!)
- Suspension Work (e.g., shocks, control arms): $200 – $1,000+ (or more!)
- 4×4 System Repair: $200 – $2,000+ (very wide range depending on what’s wrong)
Important Considerations:
- Jeep Tax: Be prepared to pay a “Jeep tax” on some parts and labor. Jeeps can sometimes be more expensive to work on due to their design and off-road focus.
- Off-Roading Costs: If you off-road your Jeep, expect maintenance and repair costs to be higher due to wear and tear.
- DIY vs. Mechanic: DIY repairs can save you a lot on labor, but only if you have the skills and tools.
- Preventive Maintenance is Key: Following your maintenance schedule can save you money in the long run by preventing bigger problems.
How to get better estimates:
- Local Mechanics: Call local Jeep mechanics (both dealerships and independent shops) for estimates on specific jobs.
- Online Forums: Jeep forums often have discussions about repair costs for specific models.
- Repair Websites: Some websites provide estimates for common repairs based on your location and vehicle.

Article By: Dale Ogden
Dale is a highly respected automotive industry expert, renowned for his pioneering work in vehicle forecasting and asset management. As the founder of Check Your Spec and former Forecast Manager at CAP HPI (the UK equivalent of Kelley Blue Book), he spearheaded the development of forecasting strategies and depreciation models for internal combustion, hybrid, and electric commercial vehicles. With over two decades of experience, Dale pioneered EV forecasting models now used by major manufacturers, and has generated residual values for over 10,000 new vehicles.
Jeep VIN Decoder FAQ
I used a free VIN decoder and it said my Jeep is a Wrangler, but it doesn't say if it's a Sport, Sahara, or Rubicon. Why?
Free VIN decoders often provide only the most basic information. Jeep trim levels (Sport, Sahara, Rubicon, etc.) are crucial for determining a Jeep’s features and value, but this level of detail is rarely included in free reports. You’ll likely need a paid report or Jeep specific resources to get the exact trim level.
My Jeep is a 2004 TJ. Can a VIN decoder tell me exactly what options it came with from the factory?
While a VIN decoder can give you some information, it won’t provide a complete “build sheet” detailing every single factory option. For older Jeeps like your TJ, you might need to explore other avenues like contacting Jeep directly (though they may not have detailed records for older vehicles) or searching for build sheet services that specialize in older models.
I'm looking at a used Jeep and the VIN comes back with two different engine codes depending on which decoder I use. What's going on?
This is a red flag! Inconsistent engine codes indicate a potential problem. It could be a simple error in one of the databases, or it could be a sign of something more serious, like an engine swap that wasn’t properly documented. You should be very cautious and investigate further before purchasing the vehicle.
I've heard about "Jeep build sheets." Can I get one using my VIN?
While some manufacturers offer build sheets through their websites, Jeep (through Mopar) generally does not provide this service directly from the VIN. However, there are third-party services that specialize in researching and providing build sheet information for Jeeps, especially older models. These services often rely on historical records and may charge a fee.
Why are Jeep VIN decoders so important compared to other car brands?
Jeeps have a vast array of trim levels, engine options, special editions, and other variations. This makes the VIN much more critical for identifying a Jeep’s true configuration and value compared to a car with fewer variations. A generic VIN decoder might tell you it’s a Wrangler, but that’s not nearly enough information.
I entered my VIN and the decoder says my Jeep was made in "Toledo." Is that accurate?
Toledo, Ohio, was a major hub for Jeep manufacturing for many years. However, Jeeps are also made in other locations. The assembly plant code in your VIN will give you the most accurate information about where your specific Jeep was built.
Can a VIN decoder tell me if my Jeep has ever been modified or had aftermarket parts installed?
No. VIN decoders only tell you the original factory specifications. They cannot detect modifications made after the vehicle left the factory. You’ll need to visually inspect the Jeep or have a mechanic check it to identify any aftermarket parts.
I'm trying to decode the VIN on a classic Jeep (like a CJ). Are the codes the same as on newer Jeeps?
No. VIN coding systems have evolved over time. The VIN structure and the specific codes used on classic Jeeps are often different from modern Jeeps. You’ll need to find resources that specialize in decoding classic Jeep VINs.
Unlock accurate valuations for your car’s features in seconds – find out what your options are worth today and in the future.


